- TECHSWU
- Posts
- TECHSWU #57
TECHSWU #57
Welcome to TECHSWU, your go-to destination for all things tech that matter in your daily life!



The article highlights 32 science fiction technologies that have become a reality in the modern world. These include 3D printing, electric cars, video calls, creative AI, driverless cars, jetpacks, cloning, humanoid robots, robotic limbs, talking cars, virtual reality, food in pills, rebreathers, exoskeletons, nuclear-powered vehicles, living in space, railguns, space tourism, stealth technology, smartwatches, smartphones, real-time translation, targeted advertising, drones, mass surveillance, flying cars, wireless communication, the World Wide Web, synthetic meat, and household robots.
The author showcases how these technologies were once considered imaginative concepts but have now been realized in some form or another. The examples provided demonstrate the transformative impact of science fiction on real-world innovations.

The electric classic car market is expected to see significant revenue growth in the future, according to a report by AMA Research & Media. The report predicts various factors that will drive the market, including the increasing conversion of classic cars into electric vehicles and the popularity of electric classic cars.
Electric cars offer several advantages over traditional petrol or diesel cars, including lower emissions and cheaper refueling costs. Classic cars are seen as the perfect vehicles for electric conversions, and such conversions have led to remarkable builds.
The report also highlights a market opportunity for governments to offer affordable conversions on old cars and make use of scrapped EV batteries. Major players in the market include Marshell Green Power, Electric Classic Cars, Tesla, BYD Auto, BMW, General Motors, and Ford.

Stanley Robotics is set to launch the new version of its autonomous robot, Stan, which aims to revolutionize automated parking solutions. The upgraded version of Stan boasts a 3-ton payload and features improvements in strength, weight, robustness, speed, and design.
Stanley Robotics, a deep tech company headquartered in Paris, combines hardware and software to provide outdoor logistics solutions. Its technology involves a robot capable of lifting and moving cars autonomously, along with an intelligent storage management software.
The company aims to bring the productivity benefits of robotics to outdoor logistics. With over 400 airports represented, the 15th edition of the Airport Parking Network Event is set to take place in Istanbul from November 24-26, 2024, offering networking opportunities and insights from keynote speakers and solution providers in the parking industry.


Restaurant technology company RobotLab has unveiled new technology that allows servers to summon robots on demand and assign them to tables. The technology includes a robot-compatible smart watch called Robot on Call, which lets servers and managers call robots to a table or area in need.
Another technology called ServeSwift allows managers and servers to assign robots to tables via a QR code, allowing robots to be programmed remotely. The technology is designed to make restaurant staff more efficient by reducing the need for multiple trips around the facility.
It is already being used at several restaurants, including Area 254 in Texas. Additionally, pizza automation system Picnic Works is partnering with Roboworx to roll out their autonomous pizza stations nationally.
Givex and Brightloom have also announced new AI capabilities for personalized guest experiences, and NCR Voyix has launched a new tableside payment technology.
In this article, the author discusses the latest advancements in smart wearable technology and how they can revolutionize daily routines. The article highlights features such as activity tracking, vitals monitoring, and customization options that can enhance fitness journeys.
It also mentions the upcoming release of watchOS 12 and encourages readers to explore the developer beta to experience the latest innovations firsthand. The article raises key questions about data security, privacy implications, adapting to different lifestyles, and environmental impacts.
It also mentions challenges such as interoperability, battery life, design, and regulatory compliance. On the advantages side, the article mentions convenience, health and fitness tracking, connectivity, customization, and entertainment and productivity features.
Disadvantages include cost, data privacy concerns, dependency, compatibility issues, and potential health risks. The article recommends exploring reputable sources for in-depth reviews and news on smart wearable technology developments.
Overall, it presents an engaging and informative overview of the topic.

Chinese e-commerce company JD.com has launched JD.
Vision, a native Apple Vision Pro app that offers an immersive shopping experience using spatial computing. The app allows users to virtually "place" products in their home to see how they would fit, eliminating the need for physical store visits.
Users can interact with virtual objects to test potential purchases and receive tailored product recommendations from an AI shopping assistant. JD.
com plans to add more features to the app in the future, including virtual interior decoration, iris recognition payments, and virtual car driving. JD.
com's JD.Vision app is set to coincide with the official release of Apple Vision Pro in China on 28 June.
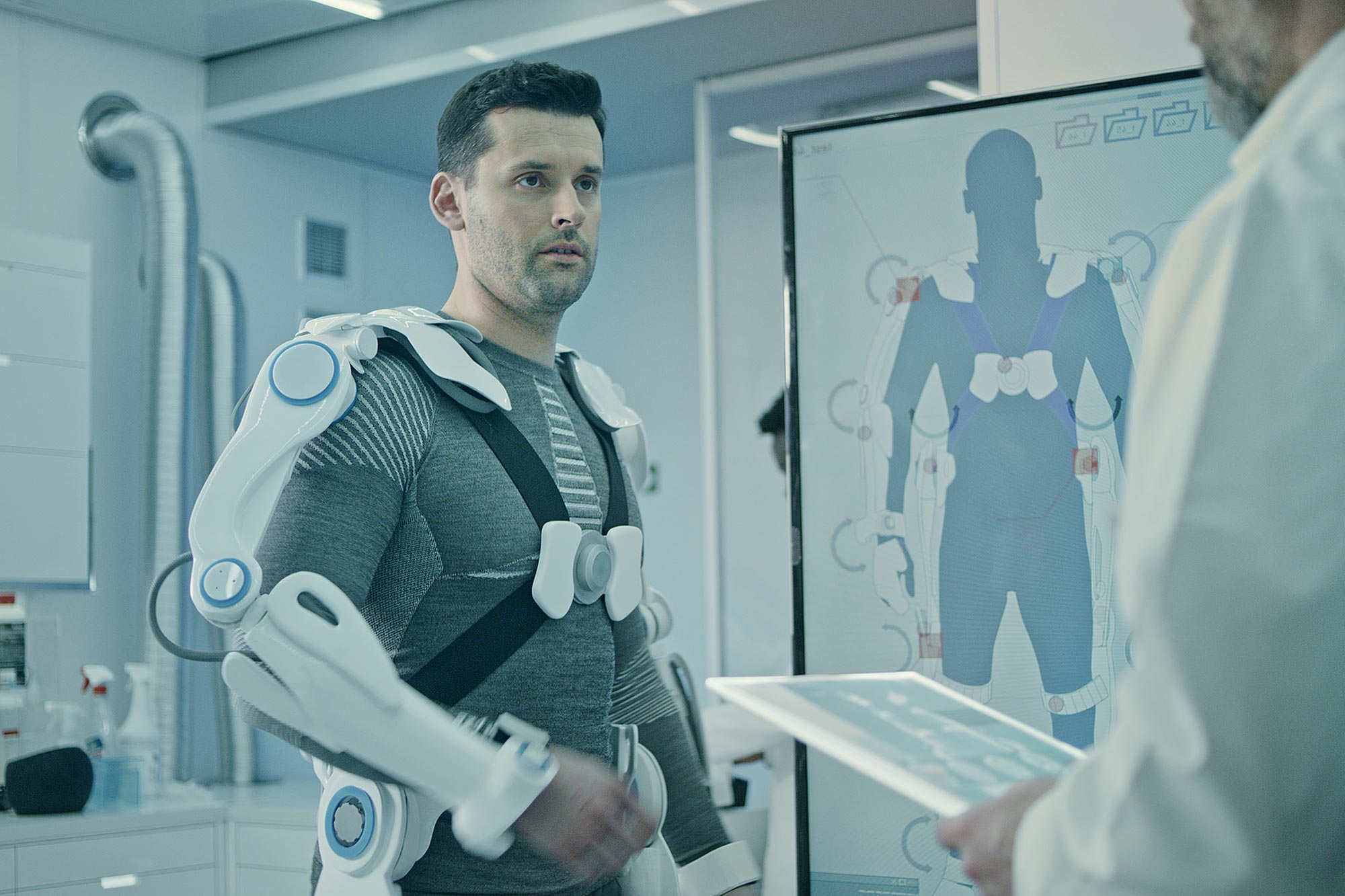

Researchers have developed an AI-enhanced controller for exoskeletons that can learn to support various human movements such as walking and running without the need for individual calibration. This breakthrough technology has the potential to significantly improve human mobility and reduce energy expenditure, making it valuable for a range of applications.
Exoskeletons are wearable robotic frameworks that aim to enhance movement, but their use has been limited due to the need for specific programming and testing on individual subjects. The new AI controller eliminates the need for human testing and can provide continuous torque assistance for activities like walking, running, and climbing stairs.
By using AI and computer simulations, the controller learns the movements and can effectively assist various individuals without the need for customization. This development has exciting implications for improving efficiency and safety for workers, astronauts, and people with disabilities.
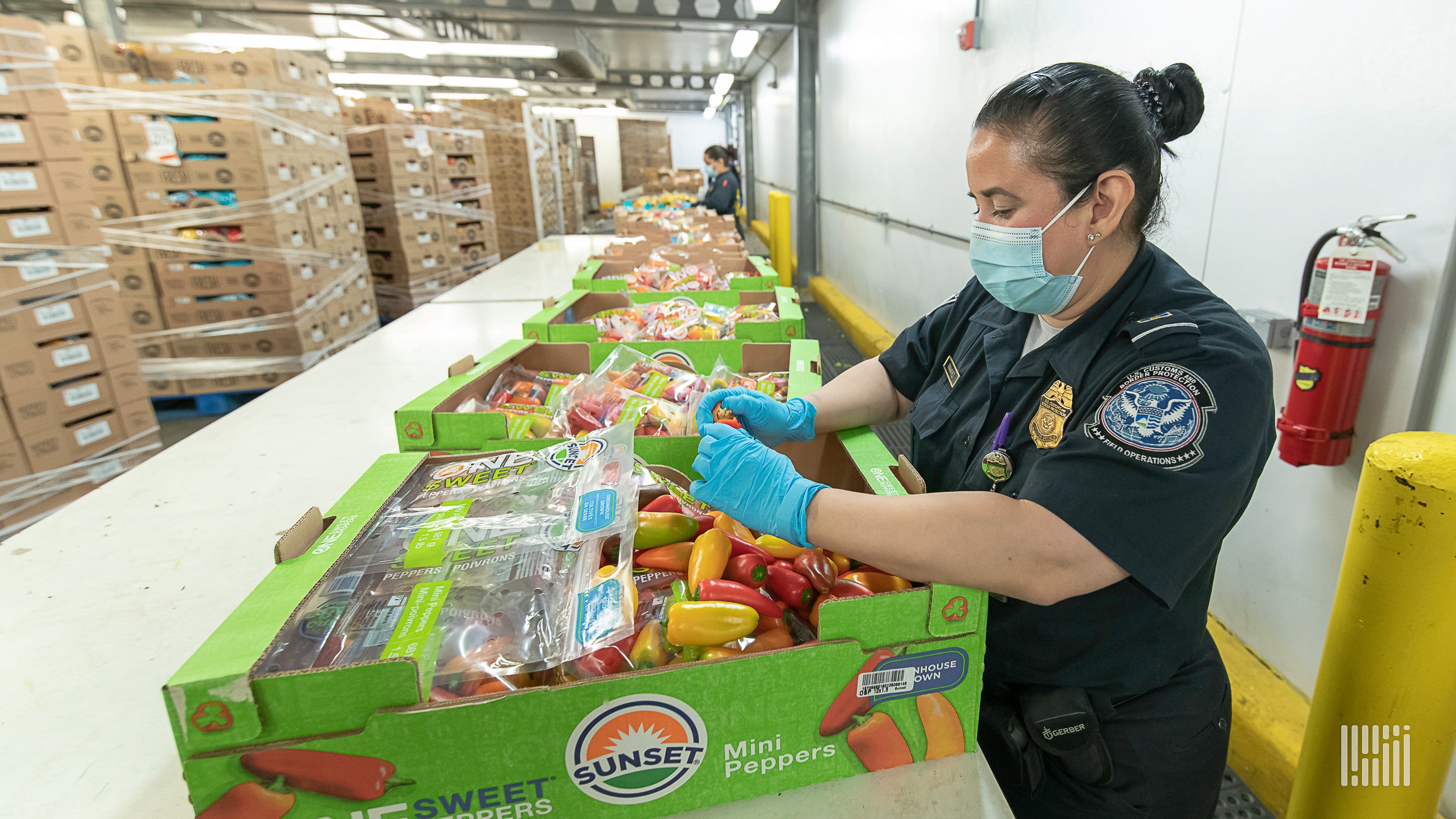


Wiliot, an Internet of Things (IoT) start-up, has launched a food safety initiative aimed at creating transparent and traceable supply chains using ambient IoT technology. The initiative, in partnership with iFoodDS and Trustwell, comes ahead of the Food and Drug Administration's new Food Traceability Final Rule, which aims to lower the risk of foodborne outbreaks and begins enforcement in January 2026.
Wiliot's ambient IoT technology allows food products to be connected to the internet at lower costs compared to RFID technology, enabling visibility and traceability throughout the supply chain. The company's devices are fully traceable, compliant, and data-driven, providing a level of efficiency, automation, quality, safety, and reputational strength.
The initiative aligns with the increasing focus on securing the food supply chain and compliance with stricter regulations.

Surfing enthusiasts have long been on the hunt for the perfect wave, but advancements in wave-generating technology have brought that search closer to home. Artificial surf pools are becoming increasingly popular as they can create waves that surfers actually want to ride.
However, the construction of these pools is not without controversy. Some of these pools are being built in drought-ridden areas, causing local opposition due to concerns over water usage.
The cost of finding or creating the perfect wave, and who will bear that cost, is at the heart of these pool-related conflicts. In other news, new research from Google DeepMind shows that AI is only capable of writing comedy to a limited extent, highlighting the limitations of AI in creative endeavors.
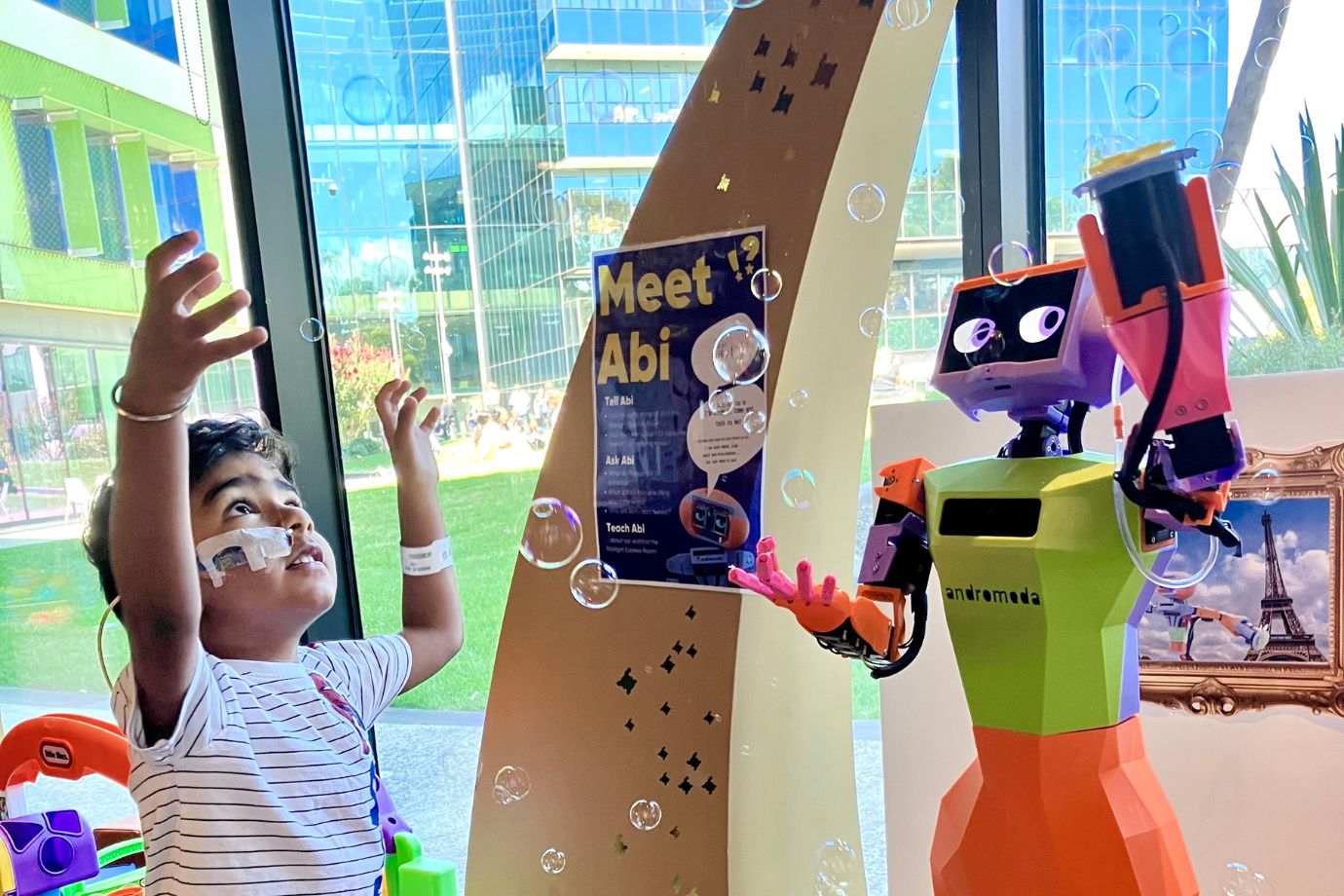


Grace Brown, a 24-year-old mechatronics engineer and entrepreneur, has closed a $3 million seed round led by Purpose Ventures for her robotics and AI startup, Andromeda. The funding will be used to scale the rollout of Andromeda's humanoid companion robot, Abi.
Abi is designed to provide joy and companionship in Australia's healthcare sector, particularly in aged care facilities and children's hospitals. The robot is already being successfully piloted, completing daily tasks for patients and providing social and cognitive support.
Abi has its own personality, with a focus on empathy and building connections with people. The investment will help Andromeda expand its team, increase the utility of Abi, and move to larger manufacturing facilities.
Brown's goal is to have 100 Abi robots in use within the next 18 months.
A new wearable brain scanner has been developed to track the brain development of children. The device, created by scientists from the University of Nottingham’s School of Physics and Astronomy, uses a novel design of magnetoencephalography (MEG) scanner to measure brain electrophysiology in children as young as two years old.
The system uses tiny sensors called optically pumped magnetometers (OPMs) which are incorporated into a lightweight helmet. The sensors detect the magnetic fields generated by brain activity and turn them into images showing which parts of the brain are engaged during different tasks.
The device is able to adapt to fit any age group and allows children to move while wearing it. The research team hopes that the new wearable brain scanner will be used to better understand the development of neurodevelopmental conditions like autism.


The University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB) has received approval from the Alabama Commission on Higher Education to offer a new graduate program in artificial intelligence (AI) in medicine. The program, set to launch in January 2027, will be the state's first AI-focused medical degree and aims to meet the growing demand for AI in the healthcare industry.
The program will train healthcare professionals in AI applications in medicine, including deep learning, computer vision, and large language modeling for healthcare data. UAB's Chief Innovation Officer, Rubin Pillay, stated that the university will be the only institution in Alabama, as well as nationally and globally, to offer a comprehensive suite of AI training in medicine and healthcare.
The program is projected to generate tuition revenue of over $6 million and will be self-sustaining from its first year. Interested applicants will need a four-year bachelor's degree in computer science or a related field, along with a minimum GPA of 3.
0.
Biola University in California has launched an AI lab with the goal of integrating morality and ethics into artificial intelligence. The lab aims to explore the intricacies of AI and provide education, foster dialogue, and lead innovative AI projects rooted in Christian beliefs.
Biola University believes that by not engaging with AI, Christian and faith-centered institutions risk falling behind in technology. The lab emphasizes ethical discernment and wants to promote greater transparency and uphold human dignity within AI.
The lab will prioritize creating AI applications that have a positive social impact and address specific needs using faith-contextualized tools. Additionally, the lab will focus on developing AI that adheres to sustainable practices, avoids exploitation, and positively contributes to the well-being of individuals and the environment.
Biola University hopes that its commitment to Christianity will enable the lab to advance moral discernment and elevate human dignity within the realm of AI.




